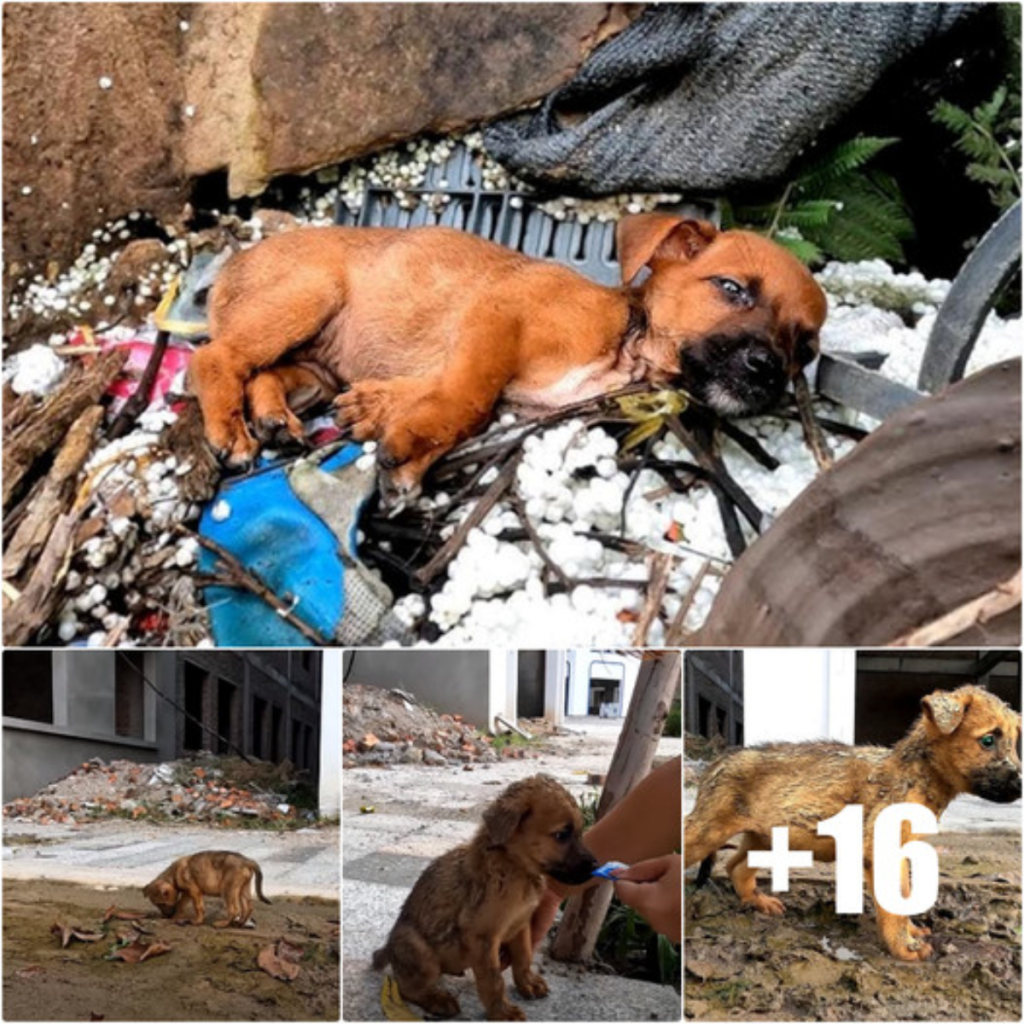

There are stories in the broad tapestry of life’s exceptional experiences that encapsulate the essence of compassion, camaraderie, and the unbreakable relationship between humans and animals. The touching story of my dear friend’s rescue of a small puppy from the midst of a construction site exemplifies these principles.

The story begins in the frantic world of construction, which is filled with noise, dust, and machines. A tiny, defenceless puppy found herself alone in this chaotic environment, a small oasis of vulnerability amidst the concrete and steel. Her presence was almost symbolic, serving as a reminder of the great bond that exists between humans and animals. It was a pledge to protect, to nurture, to assure her safety in the face of adversity.

My companion reached out her hand, guided by an unmistakable sense of obligation, to save this frail life from the construction mayhem. She set off on an unusual quest, traversing the dangers of the construction zone in order to get to the bottom of the puppy’s plight. It was more than just a protective gesture; it was a profound act of compassion, a beacon of hope for this tiny soul despite the rigours of her environment.

The story of my friend’s puppy rescue serves as a reminder that commissions have no boundaries. It emphasises the significance of extending a helping hand and providing protection regardless of the circumstances. It motivates us to be alert and mindful of those in need, no matter how unexpected or difficult the circumstance may be.

The genuine substance of my friend’s gesture of generosity is her commitment to this puppy’s well-being. It crosses boundaries and highlights the importance of extending a helping hand and rising above the circumstances. It is a monument to the power of empathy and compassion, reminding us all that kindness can grow even in the most unlikely places.
When Disaster Hits, Dogs Come To The Rescue
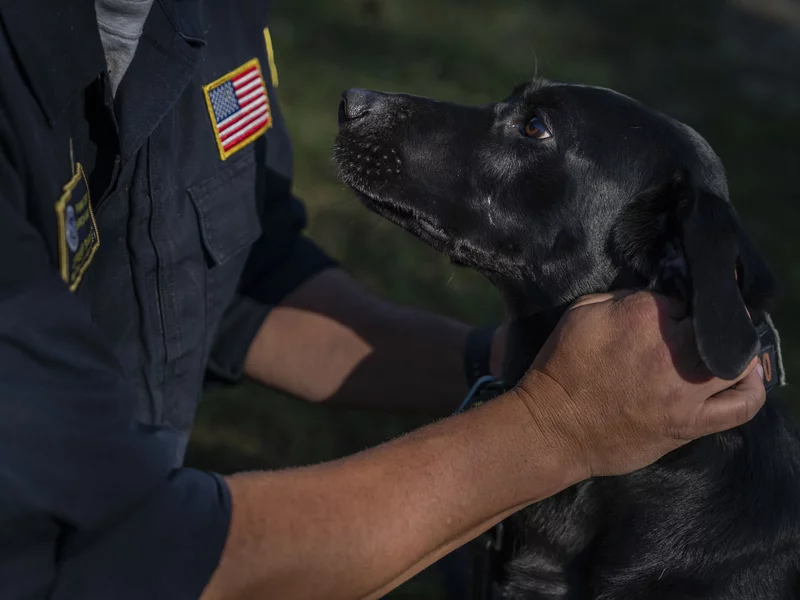

This year the U.S. has experienced devastating natural disasters.
Outbreaks of tornadoes leveled entire neighborhoods.
Flooding trapped people in their homes.
Wildfires burned out of control.
When people go missing during these catastrophes, it’s a race against time to find them alive – or their remains.
That crucial search is often carried out by specially trained dogs.
FEMA has 280 certified detection dogs trained to find people in disasters. Another 80 dogs are trained to search for human remains.
NPR’s Scott Detrow visits a Maryland training facility where dogs, and their handlers, learn skills that could save lives.


Leave a Reply